Concrete Formwork Checklist at Construction Site during Concreting and Striking
Concrete formwork is a temporary supporting structure for concrete when it is placed at the construction site to keep the concrete in position and shape till it gets hardened.
Checks for formwork should be carried out before concreting, during concreting and after removal of formwork. Concrete formwork possesses both quality and safety threats. If the formwork is not right for the concrete and work is being done at height, it may cause safety issue.
Quality of concrete is affected when the formwork is not properly aligned, not leak proof etc. Proper storage of concrete formworks is also required to for cost economy of the project.
Concrete Formwork Checklist at Site:
Formwork Checklist for Walls:
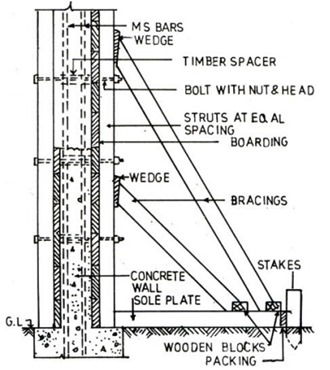
1. Ensure lateral bracings provided firmly supports the forms at all points of support.
2. Block out (stop end) braced to resist vertical and lateral loads.
3. Form panels are adequately braced and tied with each other.
4. Formwork corners shall be adequately tied to prevent leakage or bulging and spreading of concrete.
5. Ensure sufficient length is provided for wall ties and has sufficient strength and spacing as required.
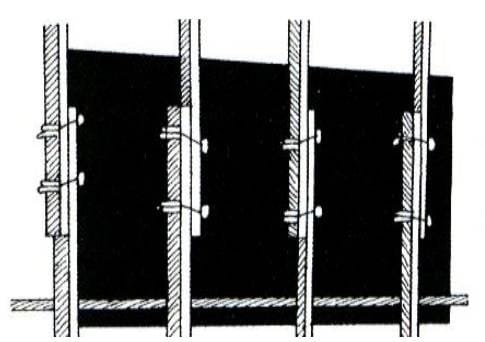
6. Check wales for proper proper spacing and joints between should be staggered from one tier to the next.
7. In double member wales, one member left continuous across the location of form ties.
8. Wall ties and bolts tightened properly.
9. In case double member wales is used, both wales should have identical depths.
10. Check for adequate lap between forms and previously cast concrete.
11. Ensure that grout leakage does not occur at joints between panels and joints between old concrete and panels above them.
12. Check the provision of resistance against uplift in case of sloping faces of concrete formwork.
13. Ensure experienced supervisor is available at site while installing the wall forms and while placing concrete.
Formwork Checklist During Concreting:
1. Before concreting commences ensure proper access for workers involved in placing, compacting and finishing concrete.
2. Presence of experienced supervisor keeping a continuous watch for any dangerous situation.
3. Adequate supply of spare props, clamps, bolts, wedges and skilled workers at site.
4. Alignment, camber, level and plumb (verticality) maintained while concreting is in progress.
5. Effective depth between top and bottom reinforcement not disturbed.
6. Cover of concrete around reinforcement steel maintained as specified.
7. Grout loss due to movement at joints and corrective action taken against it.
8. Loosening of wedges and fixings due to vibrations transmitted to the formwork and corrective action against it.
9. Spilt concrete and/or grout cleaned immediately.
10. All wooden spreaders, to hold vertical form faces apart, removed after placing concrete.
11. Wooden members for creating pockets eased before concrete sets fully.
12. Concrete pouring sequence as per that shown on formwork drawing (avoid eccentric loading).
13. Prevention of heaping of concrete and high impact drops from concrete buckets.
14. Rate of concreting within allowable limits as shown on working drawing or as assumed while designing the formwork against lateral pressures.
15. Proper bond between layers of concrete, in case concrete is placed in layers, by ensuring that needle vibrator while vibrating the top layer also penetrates the lower layer.
Checklist During Formwork Striking (Stripping or Removal):
1. Formwork design and layout such that smooth striking of formwork in sequential manner is possible.
2. Strength of concrete capable of taking self weight and construction load on it.
3. Removal time to be ascertained depending on size, shape and span of the member, grade of concrete mix and its rate of gain of strength, type of cement, ambient temperature and weather conditions and extent of curing executed.
4. At the time of removal of side form, corners and edges not damaged.
5. Ties, clamps and wedges loosened and removed gradually.
6. Removal time in line with those specified in code of practice (IS 456- 2000).
7. Props in case of beams and slabs removed in stages from mid-span working outwards.
8. Bolts, nuts, clamps, wedges collected in a box and not dropped carelessly.
9. Use of crowbars to prise open forms avoided.
10. Formwork prised loose using wooden wedges.
11. Formwork carefully lowered and not dropped and damaged.
12. Panel faces should be carefully removed and lowered without them hitting the scaffold projections.
13. Panels placed on leveled surface after removal.
14. Nail projections hammered down.
15. Cordoning off the area below the location where formwork removal is proposed.
16. Presence of competent crane operator and foreman.
Checklist for Cleaning and Storage of Formwork:
1. Formwork as soon as it is removed, cleaned with a stiff brush.
2. Dust, dirt, stubborn bits of concrete or grout removed.
3. Timber surface and uncoated ply coated with release agent before storing.
4. Steel form coated lightly with oil to prevent corrosion.
5. Damaged formwork sorted out and repaired before storage.
6. Depressions, nail holes repaired with suitable materials and lightly rubbed down to give smooth surface.
7. Panels and plywood sheets stored on a horizontally leveled floor.
8. Panels stored face to face to protect the surface.
9. Storage area protected from rain and moisture and well ventilated.
10. All formwork materials stacked off the ground.
11. Loose wailing, soldiers (struts) etc. stored with respective panels after numbering for proper match when reused.
12. Bolts, nuts, champs, pins, wedges, keys and ties stored in separate bins or boxes.
Comments