Construction in Hilly Regions – Site Selection, Planning and Design
Building construction in hilly regions requires comprehensive planning, site selection and design for slopes and sustainable concrete construction practices.
Deprived of picturesque views, fresh air and accessible flat lands in the cities, people have finally started to resort to hilly regions searching for their perfect abodes.
The economic growth and rapid urbanization in hilly regions have further encumbered the real estate development with an onus of developing multi-story buildings. Hilly regions, though tempting to construct a structure at, have wide variations in geology, geomorphology, climate, altitude and materials resources.
The unpredictable geological situations and on-going development activities, precarious climatic variation, hydrogeological conditions result in different types of hazards like landslides and mud flows in these areas which make planning and design of buildings in a hill settlement a herculean task.

Building Construction in Hilly Regions
There are four major points that should be etched into your mind when planning to construct a building in any hilly region:-
1) Construction Site Selection:
- Check for Landslide-Vulnerable areas
- Check for Slope and sequence of rock structures
- Check for existing subsurface water
- Check for existing streams
Keeping the Safety-knots of building intact on hill-site is essential and often a topic of discussions among engineers and public. The discussion intensifies every time after an incident of landslide is raised up by media. Landslides are the most prevalent natural disaster in hilly regions which increases its spatial extent day after day.
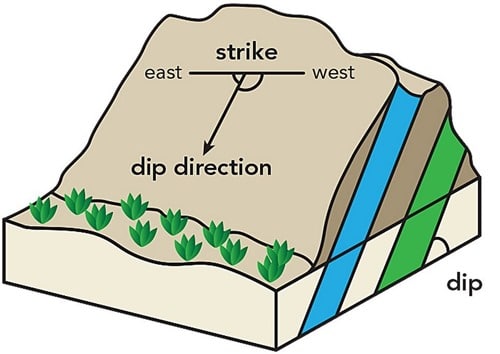
Leafing through the history of an area and assessing how it behaves in different climatic conditions could prove to be very useful and help prevent landslides. Also, awareness about how the different elements of a hill work is essential, like dip of the rock should never be towards the slope especially when the amount of dipping of such dipping planes is less than the hill slopes at the site.
The presence of subsurface water in an area may lead to the formation of cavities therefore inviting landslides. During landslide the materials like soil, rock, vegetation, and existing construction may move very rapidly within a second where as some may take longer time to develop.
The result is livelihood security lost, socio-economic condition of people destroys and a huge amount of revenue spent with untold suffer of victims after landslide occurrences.
Thus it is very important to identify the aforementioned areas before beginning any kind of construction on a hilly area.
2) Comprehensive Planning:
Garnering topographical data:
It involves detailed study of geological maps so that the engineers are aware and understand the geological formation of the site of the proposed development.
Topographic map and aerial photographs of the site and abutting areas should be examined to know the geomorphological features, previous and present land use, current development, construction activities, problem areas like previous slope failure, etc.
The knowhow of the site-histories particularly previous landslides and underground services is very important for the planning of the layouts and designs.
Site Reconnaissance
It helps confirm the information acquired from the topographical data and also to obtain additional information from the site.
For hill-site development, it is also very important to locate and study the protuberances to identify previous landslides or collapse that can act as an indicator of the stability of the existing slopes.
Site investigation
For a hill-site construction, site investigation should be carried out in at least two stages. First stage consists of boreholes and sometimes also includes geophysical survey.
The locations of the field tests should be carried out with an objective to obtain the overall subsurface condition of the site like general depth of soft soil, hard stratum and most important, the depth of bedrock.
Normally the boreholes are spread out to cover the whole site and placed at areas of potential major cut and fill. Soil samples (disturbed and undisturbed) should also be collected from the boreholes to carry out laboratory tests for the necessary soil and rock parameters for preliminary geotechnical design of the slopes, foundations and retaining walls.
In addition, the ground water profile should also be assessed. Long term monitoring of water table is also needed in sensitive and critical areas.
The general information on the subsurface profile and properties will be useful when planning the cut and fill and formation of the platform because the depths of hard stratum and bedrock will have major influence on the cost and construction time of earthworks.
Once the preliminary layout of the hill-site development is confirmed, the detailed site investigation should be carried out to obtain the necessary information for detailed geotechnical designs.
In the detailed site investigation field tests can be carried out at the following locations:
- Areas of major cut and fill.
- Retaining walls.
- Buildings or Structures with Heavy Loading.
- Layout
The planning of platform layout for hill-site development should attempt to fit the natural contour and reduce cut and fill of earthworks. If possible, try to avoid using retaining walls as this will be costlier than normal earthwork solution.
It is also very important to orientate the building layout to minimize potential differential settlement especially if the buildings are on filled ground. This can be achieved by arranging the longitudinal axis of the building parallel to the contour lines of the original topography, in which the building is underlain by fill of uniform thickness and therefore less differential settlement.
When using piles to support buildings on fill, the design engineer should evaluate negative skin friction (down drag) acting on the piles if the ground is going to settle with time.
Slip-coating of the piles with bitumen coating or surcharging of the fill to eliminate future settlement are options to eliminate the negative skin friction.
3) Design of Slopes
The phenomenon of slope failure transpires in much the same ways throughout the world with the basic causes do not differ greatly with geological and geographical locations.
Therefore, the same methods of assessment, analysis, design and also remedial measures can be applied. The solemn difference is that in tropical localities, the climate is both hot and wet causing deep weathering of the parent rocks and the slopes are of weaker materials.
For man-made slopes, there are many factors that can contribute to slope failures:
- Amiss or improper design, analysis or construction.
- High intensity rainfall
- Lack of maintenance
Therefore, for the design of the slopes, proper information on soil properties, groundwater regime, geology of the site, selection of methodology for analysis are important factors that require attention from the Engineer.
4) Sustainable development
Sustainable development is the continued ability of a society, an ecosystem, or any such interactive system to function without exhausting key resources and without adversely affecting the environment.
Construction technique should be developed with locally available, easily workable materials which are mostly environmental friendly (like timber, stone mud and bamboo) and have good climatic resistance and have little or negligible impact on environment of hill settlement.
Though cutting of trees for obtaining timber will result in loss of precious vegetation, it needs to be suitably augmented by afforestation in hilly areas.
In contrast to this, contemporary materials are manufactured from raw materials, which are available on particular locations and are transported to different parts of the country after manufacturing.
Green Building Materials for Hilly region:
- Steel framed construction
- Cement-wood-boards
- Sandwich panels (amalgamation of two fiber reinforced cement sheets)
- Aerated concrete panels
- Gypsum plasterboards
Sustainable development underscores the importance of taking a longer-term perspective about the consequences of today’s activities and of global co-operation among countries to reach viable solutions.
Comments