WALLS- TYPES, FEATURES AND DESIGN CONCEPT
Walls- Types, Features and Design Concept
FUNCTION OF WALLS
- To provide protection from weather, animal
- To divide the areas
- Act as sound barriers
- As fire walls to attenuate the spread of fire from one building unit to another
- Separate the interior spaces
- To improve the building appearance
- To provide privacy
MATERIAL FOR WALL CONSTRUCTION
- Timber, brick, concrete block, reinforced concrete can be used for wall construction.
- Good for wall construction due it’s durability, beauty and able to provide comfortable area
- Cengal is suitable to be used at hot and cold climate area
- Meranti can be used for all types of construction in the building.
- Reinforced concrete used for precast concrete panel
WALL CLASIFICATION
There are 2 types of wall that is:
a) Load Bearing Wall
Able to carry the load from above (own weight & load from roof) and transfer it to the foundation.
b) Non Load Bearing Wall
Only carry their own weight
LOAD BEARING WALL
It can be exterior wall or interior wall. It brace from the roof to the floor.
- Pre Cast Concrete Wall
- Retaining Wall
- Masonry Wall
- Pre Panelized Load Bearing Metal Stud Walls
- Engineering Brick Wall (115mm, 225mm)
- Stone Wall
- As the height of the building increased, required thickness of wall and resulting stress on foundation will also increase and cause it to be uneconomical.

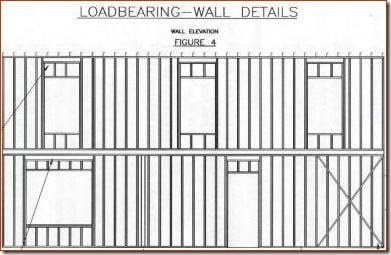
Able To Carry Other Structure Weight Beside Its Own Weight

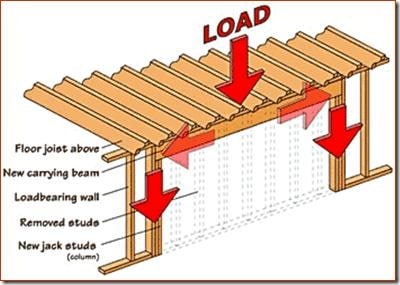
Removing a section of a load bearing wall to create a pass-through requires adding a new beam and columns to support the floor above.
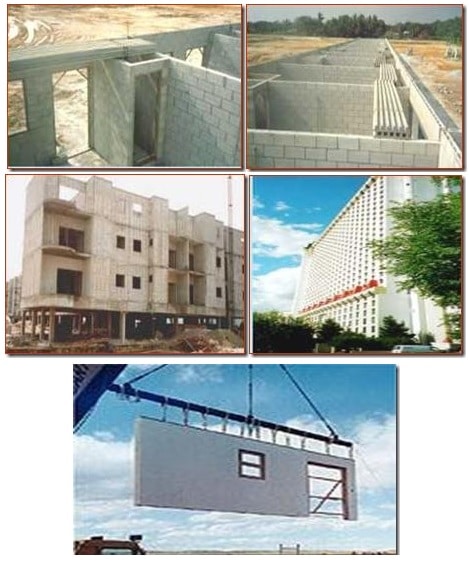

Fig: Precast Concrete Wall (Load Bearing Wall)

Fig: Pre Panelized Load Bearing Metal Stud Walls



Fig: Stone Wall (Load Bearing Wall)

Fig: Precast Concrete Wall (Load Bearing Wall

Fig; Masonry Wall

Fig: Load Bearing Retaining Wall
NON LOAD BEARING WALL
- known as interior wall (doesn’t carry other load than its own load)
- Types of non load bearing wall
a) Hollow Concrete Block
b) Façade Bricks
c) Hollow Bricks
d) Brick Wall (115mm, 225mm)



Fig: Brick Wall (Non Load Bearing Wall)

Fig: Semi Hollow Brick (Non Load Bearing Wall)

Fig: Façade Brick Wall (Non Load Bearing Wall)

Fig: Hollow Concrete Block Wall (Non Load Bearing Wall)
BRICK’S BONDING
- Stretcher Bond
- English Bond
- Flemish Bond
- Raking Bond
- English Garden Wall Bond
- Common / American Bond
- Flemish Garden Wall Bond
- Running Bond
- Herringbone Bond

Fig: Header: A brick which is laid in a way that only the short end is visible in the wall

Fig: Stretcher: A brick which is laid in a way that allows only the longer side of the brick to be exposed.



Fig: Flemish Bond
Alternate bricks are placed as header and stretcher in every course. Each header is placed centrally between the stretchers immediately above and below. This is not as strong as the English bond at 1 brick thick . Can be successfully applied in cavity wall.



Fig: English Bond
Alternative courses of headers and stretchers; one header placed centrally above each stretcher. This is a very strong bond when the wall is 1 brick thick (or thicker). One of the strongest brickwork bond patterns.



Fig: Stretcher Bond
Easiest bond to lay & minimizes the amount of cutting required. Originally used for single brick walls, now called 1/2 brick walls it became the obvious choice for cavity walls as less cutting was required.

Fig: Raking Bond
Herringbone and diagonal bonds can be effective within an exposed framed construction, or contained within restraining brick courses.


Fig: English Garden Wall Bond
An alternative version of English bond with header courses being inserted at every fourth or sixth course. This is a correspondingly weaker bond. Suitable for free standing wall.

Fig: Common / American Bond
A brickwork pattern in which all rows are stretchers, except an eighth row of headers

Fig: Flemish Garden Wall Bond
In this variant of Flemish bond, one header is placed at every third stretcher

Fig: Running Bond
Consist of all stretchers. No header used in this bond so metal ties are used. Cavity wall construction & veneered walls of brick.

Fig: Herringbone Bond
It is a purely decorative bond. It is used in floor and wall panels.
CAVITY WALL
- “A wall constructed in 2 leaves / skins with a
space / cavity between them” - “A type of building wall construction
consisting of an outer wall fastened to inner
wall separated by an air space”
FUNCTION
To prevent the penetration of rain to the internal surface of the wall
To prevent the penetration of rain to the internal surface of the wall

SHEAR WALL
- A framed wall designed to resist lateral wall. It is a vertical elements of the horizontal
force resisting system - It is used to resist wind and earthquake loading on a building.
- It is typically a wood frame stud walls covered with a structural sheathing material
like plywood.

WALL FAILURE
Vertical bowing and horizontal bending or collapse of wall is usually caused by the wall not resisting vertical pressures from foundation or upper floors & roofs or horizontal pressures from strong winds and retained earth.
Usual cause for failure of wall are as follows:
– Overloading the wall, deflection of beam above the wall will affect the wall below.
– Foundation failure
– Earthquake
– Timber pest damage weakened the timber wall
– Poor workmanship (improper brickwork)

Fig: Brick Wall Crack

Fig: Brick Wall Failure At The Roof Level

Fig: Cracked Wall

Fig: Failure In Brick Wall

Fig: Wall Failure Due To Earthquake
Comments