Highway Sound Barrier Masonry Walls -Purpose, Advantages and Design Considerations
Highway sound barrier walls works as a sound energy absorber before sound reaches the receiver. Purpose, advantages and design of sound barrier masonry walls is discussed.
Highway Sound Barrier Masonry Walls
Following points are discussed regarding highway sound barrier masonry walls:
- What is a highway sound barrier wall?
- What is transmission loss?
- What is insertion loss?
- Purpose of highway sound barrier masonry walls
- Advantages of highway sound barrier masonry walls
- Design considerations of highway sound barrier masonry walls

Fig.1: Sound Barrier Masonry Wall

Fig.2: Highway Sound Barrier Wall
What is a Highway Sound Barrier Wall?
It is a wall that works as a sound energy absorber before sound reaches the receiver. So, the mission of the sound barrier wall will not be completed unless it absorbs required amount of acoustic energy.
The acoustic energy transmission though sound barrier wall depends on several parameters, such as material density and stiffness used the construction of the wall, the angle of sending sound energy, and the range of sound frequency.
What is Transmission Loss in Sound Barrier Wall?
Transmission loss is a term used to describe the ability of materials to transmit noise and it is associated with the ratio of sound energy at its source to the transmitted sound energy.
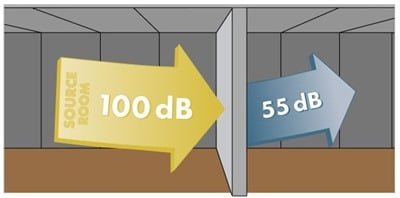
Fig.3: Transmission Loss in Sound Barrier Wall
Considering highway noise and other noises in highway noise range, the transmission loss of sound barrier materials increases as the weight of material barrier surface is increased.
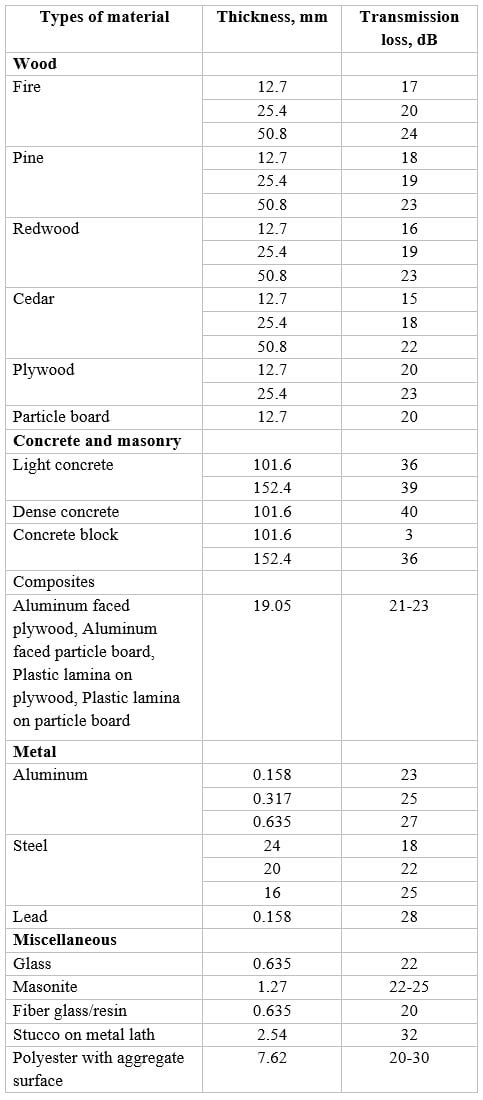
Table-1 provides transmission loss for different types of materials barrier for different thickness of barriers, and masonry transmission loss can be compared with other types of materials.
Table-1: Transmission Loss for Different Type of Material Barrier
What is insertion loss in Sound Barrier Wall?
Insertion loss is a measure of sound barrier effectiveness and it is the difference between the sound prior to the barrier placement next to the highway and after the barrier is constructed close to the highway.
The insertion loss consists of five components which are provided by NCMA TEK and the components include:
- Barrier attenuation because of sound wave diffraction around and over a barrier fixed in the line of sight plane between the receiver and the source of the sound.
- Transmission loss of sound through the barrier
- Decrease in barrier attenuation due to number of reflections as a consequent of double barrier.
- Attenuation protection through from other barriers between receiver and the source of the sound.
- Excess attenuation loss already received from soft ground cover.
Purpose of Highway Sound Barrier Masonry Walls
The prime reason that motivates highway sound barrier masonry wall construction is the decrease of dangers that occupants in the large cities are exposed to. The source of the noise is usually vehicle traffic with great speed and large volume that cross urban areas.
To decrease the level of the noise, the provision of noise abatement treatment in terms of acceptable noise diffraction and transmission loss will be required.
Federal aid highway program manual suggests various noise abatement strategies which involves procedure for managing traffics, changing vertical and horizontal alignment, obtaining property right for the placement sound reduction equipment or building sound abatement, and finally noise reduction construction of device placement disregard of outside or within highway right of way.
Advantages of Highway Sound Barrier Masonry Walls
Concrete masonry is the most broadly utilized material that is used for construction sound barrier walls.
The concrete masonry has various desirable characteristics and properties for instance flexibility in the design, excellent durability, good structural capacity, and both construction and service life maintenance cost are considerably small.
Concrete masonry is available in various shapes, color, and surface texture. This is exceptional and incomparable aesthetic characteristic of the concrete masonry, that is very hard to find materials with similar features, and because sound barrier wall is a major component of highway that is why concrete masonry can play a considerably significant role in improving the aesthetic appearance of the highway.
Apart from all beneficial characteristics mentioned above, the most superior and advantageous property of concrete masonry is the huge ability to absorb sounds. Comparatively, sound barrier concrete masonry is most successful and better in decreasing noises than other materials.
Insertion loss is a term used to describe the effectiveness of sound barrier wall and it is the difference between the level of the sound before and after the wall is constructed close to the highway.
Design Considerations of Highway Sound Barrier Masonry Walls
The design of highway masonry sound barrier is carry out like pier and panel walls or cantilever wall. Not only does the pier and panel wall is more economical due to decreased wall thickness and continuous foundation is not needed also it is simpler to construct compared with cantilever wall.
The designed panel is extended between piers. The lateral load computation for both cantilever and pier and panel wall is the same.
Comments