Workforce Motivational Theories in Construction
The various incentive measures that are applied for workforce motivation in construction industry is based on certain theories which are explained here.
Achievement of worker’s satisfaction by having a proper balance on the interrelated motivating factors brings higher performance and production of output. These factors are mainly disturbed by the prevailing nature of the construction environment. These motivational factors have an important role in the success of work carried out.
Certain theories have been put forward based on the practical conditions and needs of the employers in a construction firm. This will clearly help in understanding the need for workforce motivation and outcome by employing the same.

Workforce Motivation Theories in Construction
Following are the theories put forward by Maslow in 1987, McGregor in 1985, Vroom in 1964 and Herzberg in 1975 in order to promote workforce motivation
Maslow’s Theory of Workforce Motivation
The Maslow’s theory is based on the need and requirements of the workforce. He related the needs as a factor of motivation. He clearly explains that the needs would become a motivator if it is not satisfied.
Hence the needs that are not fulfilled will be more focused. This means if you have an employee with a series of need prioritized from lower to higher, he will pursue the higher needs only if the lower needs are satisfied.
Similarly, if we are expecting a higher output from the workers, it can be obtained only by satisfying or clearing their basic needs of problems that they have found important.
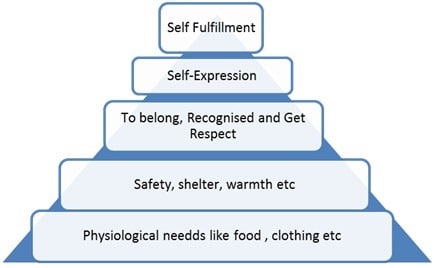
Fig.1: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in Workforce Motivation
The physiological needs are the basic needs of the human required for the survival. They involve food, sleep etc. The safety need from the second main requirement of having proper shelter and lead a safer life.
The social needs involve the need for belonging to a group from where a kind of affection, care is gained and received.
The self-expression needs involve the esteem needs where a respect to one is gained. Self-fulfillment or self-actualization involve development of the personnel to full potential.
This hierarchy means that if the lower level needs are not satisfied, they try to attain that first before going to the top ones. They focus on the top levels, only when the below one is fulfilled.
Once the theory is clear, it is advised to apply that to the work team as a responsible project or construction manager of a work team in construction.
Understanding the work team members and their needs will make you responsible to motivate. It is required to satisfy the basic needs of the teams when it is planned to build a team. If some kind of motivational issue is encountered, we have to find out if any lower needs are not satisfied or not. If it is genuine and required, it has to be met.
Below are certain employee motivation techniques that can be applied in the construction industry:
- In case of Physiological needs, it is recommended to provide proper input for the employees’ salaries and bonuses.
- The second need is to take care of the worker and the employer in terms of safety. Give them correct tools and train them for the work intended to do. Bring a comfortable environment for them to work.
- As a part of social development, scheduling seeking meetings and discussion can help in interacting and communicating one’s problem. Give proper consideration and share appreciation of a project success or target completion.
- Improve the self-confidence of the employees and workers by giving motivational awards to team who have work best. Make them realize that they are the key elements for the success of the project. Reward their hard work. This will increase their interest to work for the company.
- It is necessary to understand each member’s professional goals. Then help them to improve. This will help them satisfy their self -actualization needs.
Project managers in construction are highly recommended to make use of Maslow’s theory. This theory helps in keeping the team motivated and removes issues.
Mc Gregor Theory of Workforce Motivation
Mc Gregor put forward the X and Y theory. He believed that the managers try to motivate the employees and the workers based on whether they carry a negative or positive view of the human beings.
The negative view brings the X theory and the positive is the Y theory. He later stuck on to Y theory suggesting that the Y theory will help the work to be natural. This will make the people wish to achieve the goals by themselves. They will seek the responsibilities when they are motivated.
The X theory makes the workers to be self-centered and will lack the ambition. They won’t like taking responsibilities and are potentially indolent.
Mc Gregor found the Y theory to be more suitable for the success and the motivation of the workforce compared with the X theory. The assumption in X theory and Y theory are explained below:
X theory Assumption:
- An inherent dislike of responsibility is shown by an average human being. He tries to avoid the responsibility if he has a choice.
- Work dislike will make them to be pressurized and threatened in order to work harder
- A worker dislike responsibility. They prefer to be directed and get security.
Y theory Assumption:
- The physical and mental effort is considered as a part of natural human function.
- The commitment of the worker towards the organization is increased with the satisfaction of their basic needs
- A worker desired to seek responsibility and opportunity. He believes this would increase his creativity and ingenuity to the organization.
Vroom’s Process Theory of Workforce Motivation
According to Vroom, individual motivation is influenced by three factors. They are the:
- Self Judgment
- Perception
- Having Interpretation of comparative treatment
The process theory mostly determines how the motivational behavior is sustained in a working environment. The motivational force is measured in terms of:
- Valence
- Instrumentality
- Expectancy
The valence means the valued reward. How extend the worker who have a role in the success of the project have been rewarded is measured. More the reward to the work more is the motivational force that the worker is gained.
The second factor of instrumentality measures the performance. This means that if the rewards and the penalties incurred to the workers are linked with the performance level, then there is increase of motivational force observed in the workers.
The third factor is the expectancy, which is the perceived relationship between the effort and the performance. It will lie in a large extend within the job or within the individual relation between the working members.
Herzberg Theory of Workforce Motivation
A study was conducted by Herzberg with 200 engineers and accountants. They were told to recall incident at work that either increased on reduced their satisfaction. The effect on their attitudes and performance were studied.
The responses obtained are hence categorized under two criteria:
- Hygiene factors
- Motivator Factors
The hygiene factor is mostly related to the working environment and those factors which are extrinsic to the work. These factors will affect the dissatisfaction.
The motivator factor is related to the working content alone. The strength of these factors will affect satisfaction.
Thus, Herzberg explained that if the company have no adequate hygiene factors, the workers and the employees are considered dissatisfied even if they are paid with adequate salary and working conditions. The hygiene factors include the following factors:
- Working conditions
- Relationship and communication with the superiors
- Company policies
- Salary
Influence of Motivational Theories in the Construction Industry
The need for higher productivity in the construction industry have led to decision of implementing motivational theories in construction management. Based on the theories of motivation financial motivators, semi financial motivators and non-financial motivators can be employed.
The financial motivators as the name says will involve having cash rewards. These motivators have the closest connection between the efforts of an individual or the performance with their pay. Two types of the same are used i.e. the piece rate system and the standard hourly rate.
In case of a piece rate system, a work is set to be completed within a specific fixed time period and a standard rate. The piece rate is hence calculated by dividing the base wage by the standard rate. For a production beyond the standard, this base piece rate will act as the incentive.
To fill the gaps between the companies and the worker’s objectives, semi financial motivators were developed. This will help to establish a mutual loyalty and commitment on both the sides.
This concentrates on benefits like the staff canteens, sports facilities, pension schemes, temporary bus, expense accounts, luncheon vouchers etc. These help in satisfying the needs as specified by the Herzberg theory and the Maslow’s higher needs.
The non-financial motivators are more in satisfying the Maslow’s higher needs and the Herzberg’s motivating needs. It specifies the methods to be given to develop and understand the importance of the individual, self expression, self-fulfillment, understand the need for involving in group participations that can give social satisfaction.
Comments