REQUIREMENTS OF UNDERGROUND (BASEMENT) WALLS
Underground or basement walls are required to be constructed in case of underground water tank, basement parking, as a store room and many other purposes. These underground or basement walls are exposed to many types of loads and forces, moisture due to presence of ground water or due to rains etc.
Underground walls must support following functional requirements whether it is in a framed structure or load bearing structure:
- Structural Stability
- Durability
- Moisture exclusion
- Buildability
The presence of salts, high water table interfere with the construction process of the building, and it also affects the durability. These problems create restrictions on the nature of construction of walls below ground level and it is particularly important in case of basement to be used as internal building space.
Due to moisture conditions in case of high water table, materials with low porosity are to be used. Porous materials absorb moisture from the ground and expand on freezing, causing spalling and friability of the material. Non-porous materials also tend to perform better in terms of moisture exclusion, since they do not transfer moisture through capillarity.
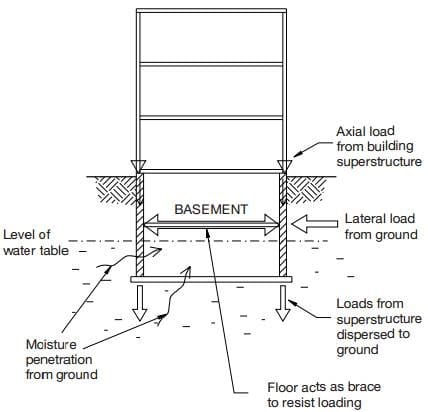
The underground walls are subjected to high pressures, both axially and laterally. The lateral force exerted by the mass of earth which surrounds the walls can have a considerable effect, particularly in the case of walls to deep basements. These lateral loads must be adequately resisted if the stability of the wall is to be maintained. This is generally done either by bracing the walls or by constructing walls that are sufficiently robust to cope with the stresses involved.
To resist this loading, bracing walls below ground level with temporary supports or to utilise the floors of the buildings as permanent braces. Also, walls can be constructed to minimise the ground pressure by bracing them gradually as the work proceeds.
Comments